How to Gain Weight with a Fast Metabolism

Weight gain with a fast metabolism feels like an uphill battle. No matter how much you eat and how many calories you consume in surplus, you just don’t seem to gain weight as you expected.
You can eat as many calorie-dense fast foods as you want but none of that would work for weight gain unless you make some lifestyle changes. In this blog, I will share the differences between slow and fast metabolisms, why they affect weight gain, and provide actionable strategies to gain weight with a fast metabolism.
How Metabolism Affects Weight Gain
Have you ever wondered why some people seem to eat whatever they want without gaining weight, while others struggle to shed even a pound? The answer lies in our Basal Metabolism Rate—the rate at which your body converts food into energy.

Slow vs. Fast Metabolism
Metabolism refers to the rate at which our bodies burn calories to sustain vital functions like breathing, circulation, and cell repair.
Individuals with a slow metabolism burn fewer calories at rest, making it easier for them to gain weight if they consume more calories than they burn. Conversely, those blessed with a fast metabolism burn calories at a quicker rate, making weight gain a challenging endeavor.
The primary challenge with a fast metabolism is that your body expends energy rapidly and consumes all available calories. After that, your body switches to metabolising your fat reserves “Glycogen” to meet high energy demand due to fast metabolism. This energy surplus makes it difficult to achieve a calorie surplus necessary for weight gain.
Why do you have a fast metabolism? Fast metabolism is linked to your genetics, hormonal imbalances, and lifestyle habits. Click here to our guide to women with PCOS
7 Proven Strategies to Gain Weight Fast
Go in Calorie Surplus
Your body needs energy (measured in calories) to perform its daily functions. An average human’s daily caloric intake is anywhere between 3000–3500 calories per day.
Eat More Calories = Weight Gain

What to Do:
Calculate your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) using online Calorie-In and Calorie-Out calculators. The calculator will tell your ideal calorie intake based on your BMR. Consume 500-1000 calories more than your BMR each day.
You can also use the BMR formula:
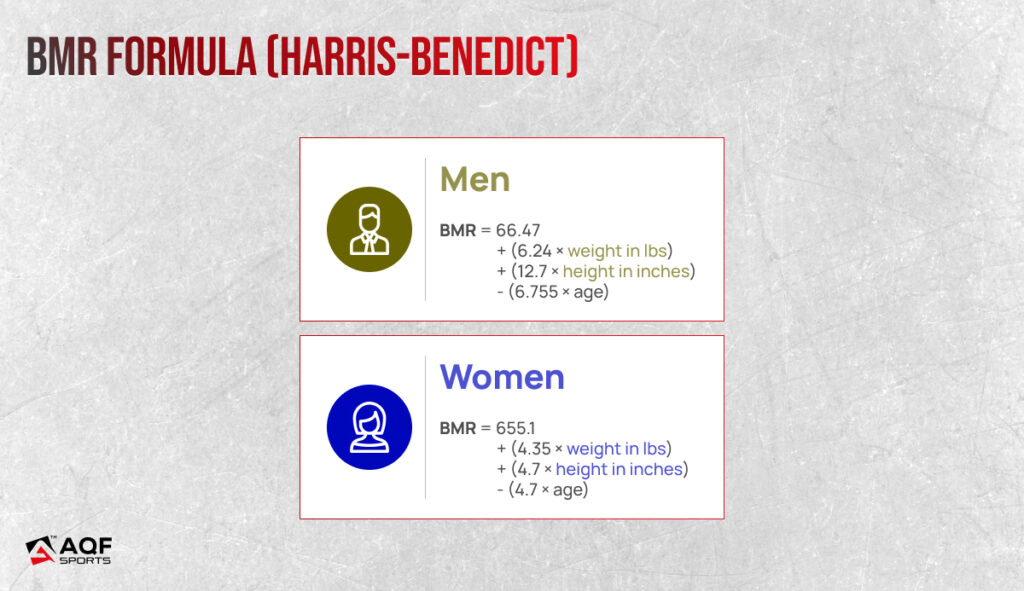
A caloric surplus provides the necessary energy for muscle growth and weight gain, ensuring you have sufficient fuel to support your body’s metabolic demands.
Distribute your calorie intake across multiple meals and snacks throughout the day to maintain a consistent energy surplus.
Strategic meal timing ensures a steady supply of nutrients to support muscle growth, recovery, and sustained energy levels throughout the day.
Increase Your Protein Intake
Protein isn’t just for bodybuilders; it’s essential for anyone looking to gain weight. You should be eating 1.0 to 1.6 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily. Eat protein-rich foods such as
- Chicken
- Turkey
- Fish
- Eggs
- Greek yogurt
- tofu, and
- legumes
These foods provide the amino acids your muscles need to grow and repair. Choose lean protein sources and unsaturated fats to support muscle repair, growth, and overall health.

Protein supports muscle repair and growth, while healthy fats provide sustained energy, promote satiety, and support hormone production.
Supplementing your diet with whey protein can also help meet your protein needs conveniently.
Add Healthy Fats in Your Meal:
Healthy fats are your ally in the battle against a fast metabolism. These fats not only provide valuable calories but also support hormone production, joint health, and overall well-being.
Opt for omega-3 fatty acids rich foods, such as
- Avocados
- Nuts
- seeds,
- fatty fish.
- Olive Oil
Include Complex Carbs in Your Diet:
Carbohydrates are not the enemy—they’re your body’s preferred energy source, especially during intense workouts. Eat complex carbohydrates like:
- whole grains
- brown rice
- sweet potatoes, and
- legumes.
These nutrient-rich carbs provide sustained energy and replenish glycogen reserves in your body. Glycogen production is the body’s preferred fat storage mechanism. It also facilitates muscle growth and bulking.
Bulk Training
Strength training isn’t just for sculpting muscles; it’s a potent stimulus for weight gain. Perform compound exercises like squats, weightlifting, deadlifts, bench presses, and rows into your routine. Aim for 3-4 sets of 6-12 repetitions with challenging weights for effective bulk training results.
Allow Downtime in Your Routine
Rest and recovery are integral parts of the muscle-building process. You should get at least 7-9 hours of sleep per night. During workouts, allow adequate rest between sets and incorporate rest days into your training schedule. Rest periods allow your muscles to repair, rebuild, and grow stronger.
Incorporate stress-reducing activities such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or spending time in nature to create a relaxing sleeping environment. Avoid caffeine and heavy meals close to bedtime. Instead, opt for sleep-promoting foods like chamomile tea, warm milk, bananas, and complex carbohydrates.
Quality sleep and stress management optimize hormonal balance, reduce cortisol levels, promote muscle recovery, enhance metabolism, and support overall health and well-being.
How to Gain Weight on Face?
Just like spot fat reduction, It’s not possible to gain weight on any one part of your body. However, some facial exercises can help tone and define your facial muscles for a bulkier appearance. Here are some facial exercises you can try to promote weight gain on your face:
- Cheek Lifts
- Jaw Movements
- Puff Cheeks
- Tongue Press
- Fish Face
- Chin Lifts

How to Gain Weight on Legs?
Leg weight gain requires a combination of diet surplus, good protein intake, proper meals and regular exercises. The following exercises can promote weight gain in legs:
- Squats
- Lunges
- Deadlifts
- Leg Press
- Calf Raises
- Leg Extensions
- Hamstring Curls
Final Word
Weight gain with a fast metabolism is a bit challenging but you can get a bulkier appearance by implementing strategic nutrition, incorporating strength training, optimizing meal timing, prioritizing sleep and stress management. The key is going into calorie surplus and taking balanced meals.
Reading List






