Benefits of Zone 2 Cardio – All You Need to Know

What if you could exercise comfortably for longer durations and reap incredible fitness benefits? Zone 2 cardio: a moderate intensity level that might just be the key to your fitness goals. But what exactly is it, and what can it do for you?
Zone 2 cardio is a specific intensity level during exercise which elevates your heart rate. Picture it as a comfortable, conversational pace—challenging enough to elevate your heart rate, yet not too intense to make talking difficult.
Zone 2 Cardio Meaning
Zone 2 cardio is a training intensity level within a structured heart rate zone aimed at improving endurance and maximizing fat burning during aerobic exercise.
It is often referred to as the “fat-burning zone” because it primarily uses fat as a fuel source during exercise.
Zone 2 workouts are longer, ranging from 30 minutes to over an hour, focusing on maintaining a steady, manageable intensity.
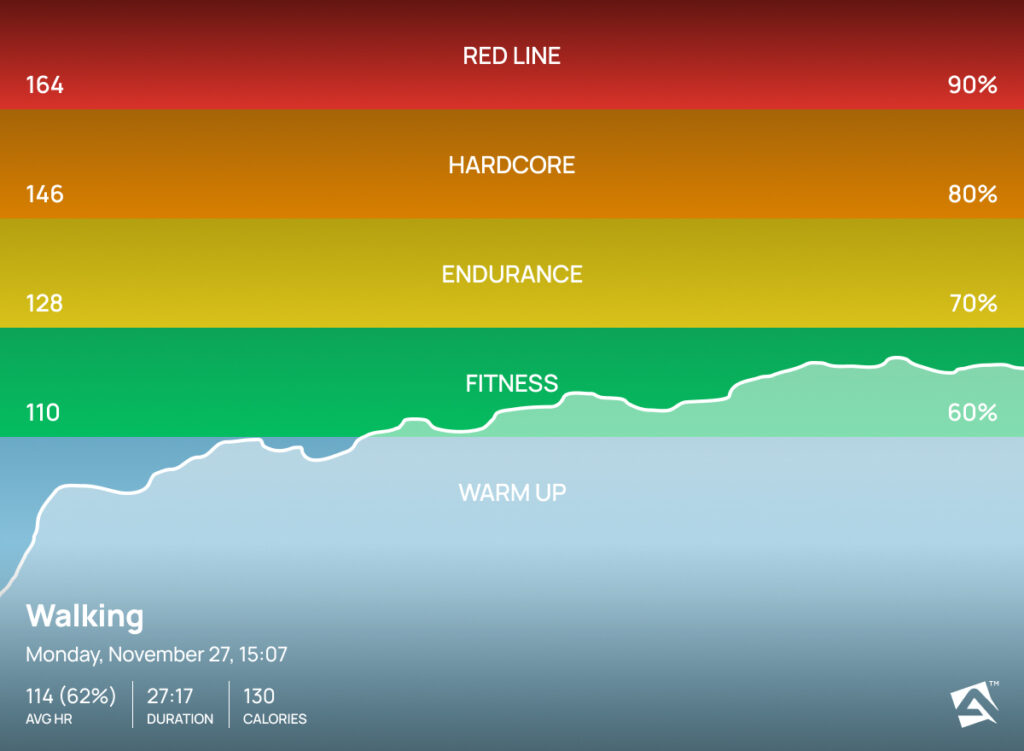
Zone 2 Cardio Heart Rate
This cardio is characterized by a moderate intensity level that pushes your heart rate to around 60-70% of your maximum heart rate. It builds a steady activity pace for sustainable fat burning results.
Zone 2 Cardio Examples
Activities that keep you in this zone include brisk walking, steady cycling, light jogging, or swimming at a consistent, moderate pace.
Benefits of Zone 2 Cardio
Boosts Aerobic Capacity:
Zone 2 training enhances the body’s ability to use oxygen efficiently, improving aerobic capacity and endurance [1].
More Fat Utilization:
Training in this zone promotes fat metabolism, encouraging the body to use fat as a primary fuel source during exercise, aiding in weight management.
Improves Cardiovascular Health:
Consistent Zone 2 workouts positively impact heart health by strengthening the heart muscle and improving circulation.
Enhances Fitness Base:
Building a strong aerobic foundation through Zone 2 training supports improved performance in various activities and sports.

Zone 2 Cardio Accelerates Lipid Metabolism
Scientific research shows that exercising within the Zone 2 heart rate range optimizes fat oxidation without excessive stress on the body.
Zone 2 cardio, performed at a moderate intensity, primarily uses fat as a fuel source for energy production during exercise.
Zone 2 heart rate range encourages the body to optimize fatty acid oxidation. This process involves breaking down stored fats into fatty acids and subsequently utilizing them for energy.
It promotes efficient utilization of intramuscular triglycerides (IMTG) and enhances the transport of fatty acids into mitochondria for oxidation, contributing to an efficient lipid metabolism [2].
Moreover, Zone 2 training improves hormonal responses such as insulin, cortisol, and adrenaline balance which play a role in regulating lipid metabolism.
Suggested Read: Exercises for Women with PCOS
Studies have shown that training at moderate intensities, like Zone 2, for extended periods enhances the body’s ability to use fat as fuel, contributing to weight management and improved endurance.

Zone 2 Cardio Calculator – How to Find Your Zone 2
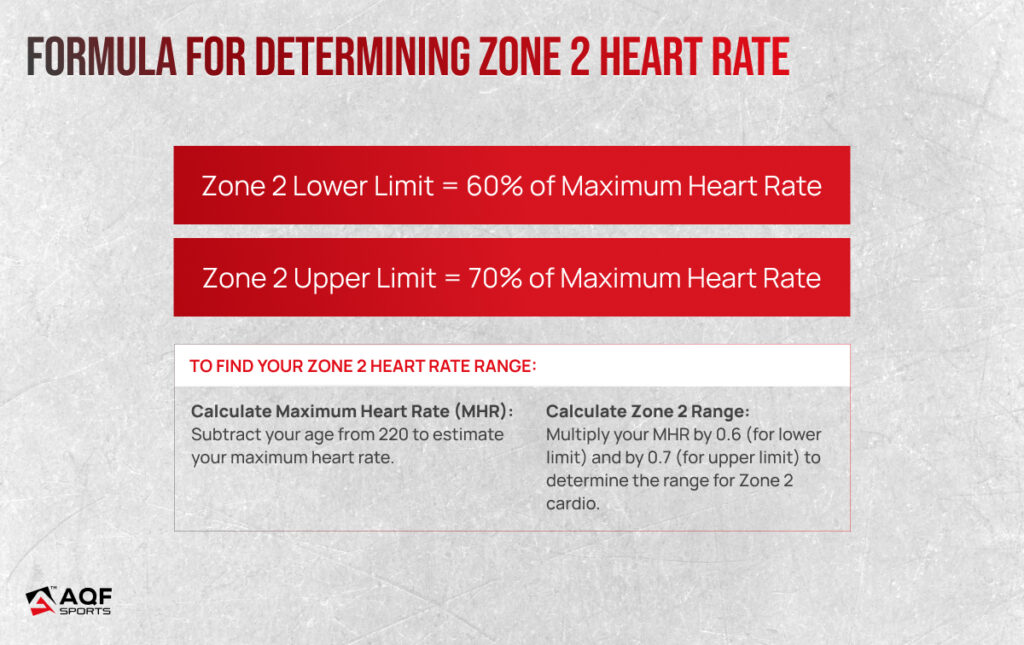
Calculate Maximum Heart Rate (MHR):
Subtract your age from 220 to estimate your maximum heart rate (MHR). For example, if you’re 30 years old, your estimated MHR would be 190 (220 – 30).

Determine Zone 2 Range:
Zone 2 typically falls between 60-70% of your MHR. Calculate 60% and 70% of your MHR to establish the range.
Use a Heart Rate Monitor:
Wear a heart rate monitor during exercise to track your heart rate. Ensure it falls within the calculated Zone 2 range.
Assess Perceived Exertion:
Pay attention to how you feel during exercise. In Zone 2, you should be able to maintain a conversation comfortably without feeling overly strained.
Experiment and Adjust:
Experiment with different intensities during workouts while monitoring your heart rate. Adjust your pace to ensure you stay within the Zone 2 range for optimal training benefits.
Daily Zone 2 Cardio Workout
Zone 2 cardio workouts primarily involve exercises performed at a moderate intensity within the heart rate range of 60-70% of your maximum heart rate. You can structure your sessions with various exercises to stay within this heart rate zone. Here’s a simple Zone 2 Cardio workout:
Warm-Up (5-10 minutes):
Start with a light activity such as walking or cycling at an easy pace to prepare your body for exercise.
Brisk Walking (15-20 minutes):
Walk at a brisk pace, maintaining a conversational effort. Swing your arms and focus on proper posture.
Cycling (10-15 minutes):
Transition to cycling on flat terrain or a stationary bike at a moderate pace. Ensure consistent pedaling without exerting too much effort.
Jogging/Running (10-15 minutes):
Move into a light jog or run at a pace where you can comfortably talk without becoming breathless. Avoid sprinting or pushing too hard.
Swimming (10-15 minutes):
Swim laps at a controlled, steady pace, alternating strokes to maintain a consistent effort.
Cool Down (5-10 minutes):
Conclude with a gentle cool-down activity, like walking or stretching, to gradually lower your heart rate.
Suggested Read: 5-Minute Full Body Cool Down Exercises – 11 Ways to Relax Your Muscles
Tips for Structuring Zone 2 Workouts:
- Rotate through various exercises to maintain interest and work different muscle groups.
- Use a heart rate monitor to ensure you stay within the Zone 2 range.
- Gradually increase duration or intensity as your fitness improves, but remain within the prescribed heart rate zone.
- Focus on maintaining a consistent, moderate effort level without pushing into higher intensity zones.
Zone 2 Cardio – FAQs
What is the best way to do Zone 2 cardio?
Engage in activities like brisk walking, steady cycling, light jogging, or swimming at a pace that keeps your heart rate within 60-70% of your maximum. Focus on a comfortable effort level where conversation remains possible.
What counts as Zone 2 cardio?
Any exercise that maintains your heart rate between 60-70% of your maximum falls into Zone 2. It includes activities like moderate-paced walks, leisurely bike rides, or easy jogs that don’t push you into higher intensity zones.
What is the formula for Zone 2 cardio?
The Zone 2 heart rate range is typically calculated based on a percentage of your maximum heart rate (MHR). The formula for determining Zone 2 heart rate is:
How long should my zone 2 runs be?
Start with 20-30 minutes for Zone 2 runs or workouts and gradually extend the duration as your endurance improves. Aim to progress gradually to longer durations while staying within the 60-70% heart rate range.
The Bottomline
Zone 2 cardio offers fantastic benefits. It’s a sweet spot for improving endurance, boosting fat burning, and building a solid aerobic foundation. By exercising in this zone, you enhance your body’s ability to use oxygen efficiently and burn fat effectively, all while keeping a comfortable pace.
Discover More Topics
- Jump Rope Length: How Long Should a Skipping Rope Be?
- Neck Harness Exercises: How to Build Thick Neck Muscles?
- Small Waist Workout (Complete Guide to Waist Trimming)
References:
[2] The Regulation of Fat Metabolism during Aerobic Exercise






